Benefits of proton therapy
It is also one of the most promising cancer therapies ever developed.1,2 With reduced radiation exposure of healthy tissues compared to other cancer treatments,3-6 proton therapy potentially reduces the risk of secondary cancers and improves the patients' quality of life. Today, It is estimated that ~15% of radiotherapy patients could benefit from proton therapy, and improve their well-being and often outcome.7-9
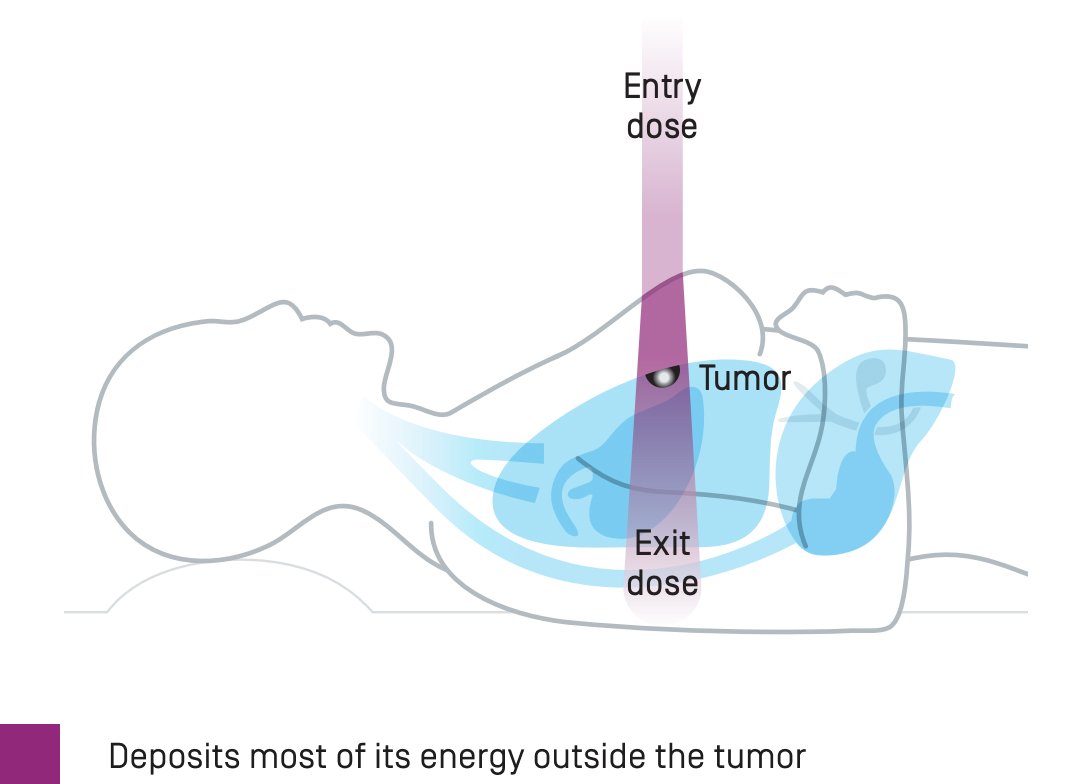
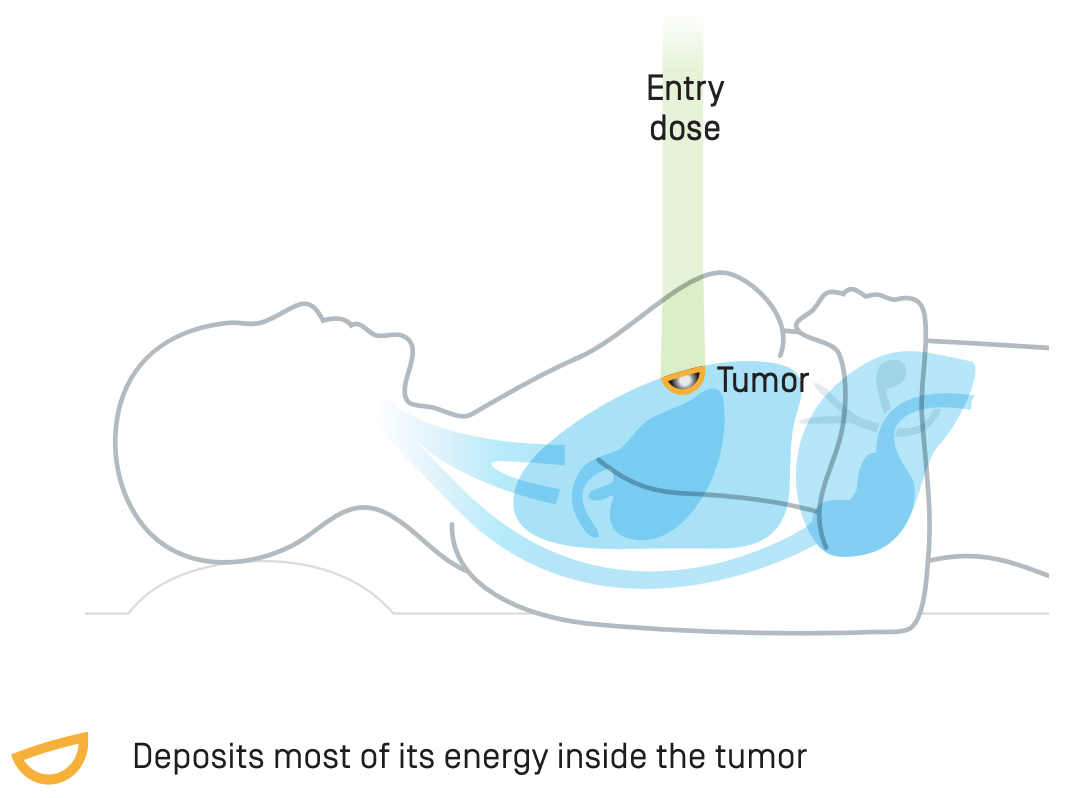
What are the benefits of proton therapy?
Minimizes radiation exposure of healthy tissues.
Lower integral dose to normal tissues.10-12
May improve the patients' quality of life.13-15
Potentially reduces the risk of secondary cancers.16-18
Widens the possibility of re-treatment with reirradiation for patients with recurrent cancer.19-21
Medical indications
Proton therapy is considered to be the most advanced radiation treatment for many forms of cancer. About 20%* of radiotherapy patients could benefit from it and it is already used to treat multiple forms of cancers. It is particularly appropriate when treatment options are limited, or unacceptable risks are noted when using other radiotherapy modalities causing greater short- and long-term side effects to patients.22
* Source: Alcimed study, "Understand, quantify and improve patients' access to Proton Therapy in the USA and Europe", November 2017
Discover the different types of cancers for which proton therapy can be a valid treatment option
IBA Proton Therapy centers worldwide
We have developed customized, made-to-measure, proton therapy solutions for more than 60 leading medical centers across the world.
Discover the centers where you can get access to IBA Proton Therapy technology.
What they say about it

The Proton Pro-Team comic book
Understanding the amazing world of proton therapy
We use our unique experience in proton therapy to help and support our customers. From developing your plans for proton therapy through to managing the life cycle of your system, we will stand by your side with one single goal in mind: provide best care to your patients.
Your proton therapy community
Campus is the most knowledgeable proton therapy community in the world. With Campus, physicians, medical physicists, dosimetrists, therapists, managers and industry partners will have the tools to share knowledge, and find the information they need at every stage of their proton therapy journey.

ProteusONE
The compact proton therapy system transforming cancer treatment
Proton therapy is the most advanced radiotherapy treatment in existence, delivered using the most powerful medical device. By harnessing the specific physical characteristics of protons, proton therapy minimizes radiation exposure to healthy surrounding tissues, potentially leading to fewer side effects than traditional radiotherapy.
References
1. Nie M, Chen L, Zhang J, Qiu X. Pure proton therapy for skull base chordomas and chondrosarcomas: A systematic review of clinical experience. Front Oncol [Internet]. 2022;12.
2. Jones B, McMahon SJ, Prise KM. The radiobiology of proton therapy: Challenges and opportunities around relative biological effectiveness. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) [Internet]. 2018;30(5):285–92.
3. Mohan, Radhe, and David Grosshans. Proton Therapy – Present and Future. Advanced drug delivery reviews 109 (2017): 26–44. Web.
4. Suit HD. Protons to replace photons in external beam radiation therapy? Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) [Internet]. 2003;15(1):S29–31.
5. Suit H, Urie M. Proton beams in radiation therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst [Internet]. 1992;84(3):155–64.
6. LaRiviere MJ, Santos PMG, Hill-Kayser CE, Metz JM. Proton therapy. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am [Internet]. 2019;33(6):989–1009.
7. Health Council of the Netherlands. Proton radiotherapy | Advisory report | The Health Council of the Netherlands. Accessed September 16, 2022. https://www.healthcouncil.nl/documents/advisory-reports/2009/12/11/proton-radiotherapy
8. Glimelius, Bengt et al. Number of Patients Potentially Eligible for Proton Therapy. Acta oncologica 44.8 (2005): 836–849. Web.
9. Orecchia R, Krengli M. Number of potential patients to be treated with proton therapy in Italy. Tumori [Internet]. 1998 [cited 2024 Apr 28];84(2):205–8.
10. DeLaney TF. Proton therapy in the clinic. In: IMRT, IGRT, SBRT. S. Karger AG; 2011. p. 465–85.
11. Ioakeim-Ioannidou M, Rose M, Chen Y-L, MacDonald SM. The use of proton and carbon ion radiation therapy for sarcomas. Semin Radiat Oncol [Internet]. 2024;34(2):207–17.
12. Lomax AJ, Bortfeld T, Goitein G, Debus J, Dykstra C, Tercier P-A, et al. A treatment planning inter-comparison of proton and intensity modulated photon radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol [Internet]. 1999;51(3):257–71.
13. Sharma, Sonam et al. Quality of Life of Postoperative Photon versus Proton Radiation Therapy for Oropharynx Cancer. International journal of particle therapy 5.2 (2018): 11–17. Web.
14. Yock, Torunn I et al. Quality of Life Outcomes in Proton and Photon Treated Pediatric Brain Tumor Survivors. Radiotherapy and oncology 113.1 (2014): 89–94. Web.
15. Laack, N.N. et al. Patient-Reported Quality of Life during Photon and Proton Radiation Therapy: Results of a Prospective Registry of Patient Reported Outcomes in a Large-Volume, Multi-Site Practice. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 102.3 (2018): e739–e739. Web.
16. Xiang M, Chang DT, Pollom EL. Second cancer risk after primary cancer treatment with three-dimensional conformal, intensity-modulated, or proton beam radiation therapy. Cancer. 2020: 126: 3560-3568. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32938
17. Eaton, Bree R. et al. Secondary Malignancy Risk Following Proton Radiation Therapy. Frontiers in oncology 5 (2015): 261–261. Web.
18. Chung, Christine S et al. Incidence of Second Malignancies among Patients Treated with Proton versus Photon Radiation. International journal of radiation oncology, biology, physics 87.1 (2013): 46-. Web.
19. Lee, Anna et al. Evaluation of Proton Therapy Reirradiation for Patients With Recurrent Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JAMA network open 6.1 (2023): e2250607-. Web.
20. Scartoni, Daniele et al. Proton Therapy Re-Irradiation Preserves Health-Related Quality of Life in Large Recurrent Glioblastoma. Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology 146.6 (2020): 1615–1622. Web.
21. Verma, Vivek et al. Systematic Assessment of Clinical Outcomes and Toxicities of Proton Radiotherapy for Reirradiation. Radiotherapy and oncology 125.1 (2017): 21–30. Web.
22. Thomas H, Timmermann B. Paediatric proton therapy. Br J Radiol [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2024 May 4];93(1107):20190601.
23. Yan S, Ngoma TA, Ngwa W, Bortfeld TR. Global democratisation of proton radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2023 Jun;24(6):e245-e254.
24. Burnet NG, Mee T, Gaito S, Kirkby NF, Aitkenhead AH, Anandadas CN, et al. Estimating the percentage of patients who might benefit
from proton beam therapy instead of X-ray radiotherapy. Br J Radiol (2022) 10.1259/bjr.20211175.
25.Terasawa T. Systematic review: Charged-particle radiation therapy for cancer. Ann Intern Med [Internet]. 2009;151(8):556.
26.Lomax AJ, Bortfeld T, Goitein G, Debus J, Dykstra C, Tercier P-A, et al. A treatment planning inter-comparison of proton and intensity modulated photon radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol [Internet]. 1999;51(3):257–71.
27.American Society for Radiation Oncology. Model Policies. Proton beam therapy (PBT). May 20, 2014; updated 2023. Accessed December 13, 2024. https://www.astro.org/ASTRO/media/ASTRO/Daily%20Practice/PDFs/ASTROPBTModelPolicy.pdf$












