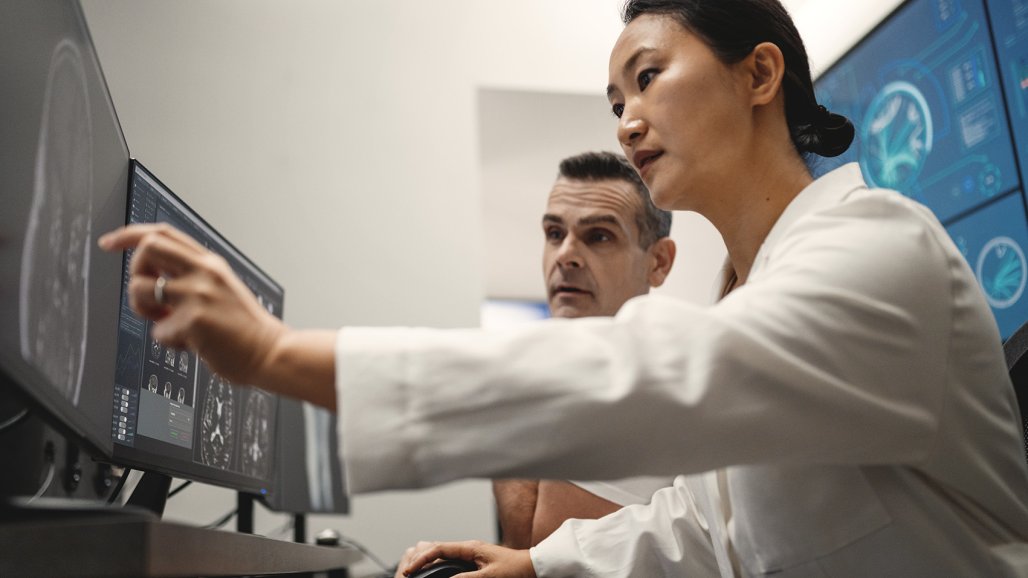
High Conformality and Reduced Side Effects
As Dr. Deraniyagala explains, “the primary benefit for patients, from DynamicARC, will be the conformal treatment, leading to less side effects long-term”. The proton Arc technology allows for highly precise targeting of tumors while sparing surrounding healthy tissue. As a result, patients may experience fewer long-term side effects, a crucial consideration in cancer treatment.3-6
DynamicARC: The Forefront of Cancer Treatment
As the medical director of the William Beaumont University Hospital, but also as a radiation oncologist, Dr. Deraniyagala emphasizes that DynamicARC shifts the paradigm of proton therapy from just being an alternative to photons of conventional radiotherapy to becoming a leading treatment modality. As Dr. Deraniyagala highlights, DynamicARC could bring noticeable benefits in terms of interplay effect, the ability to treat mobile tumors more easily, hypofractionation, and the high dose conformality for sharper treatments.3,6-9
Expanding Treatment Capabilities with DynamicARC
With the integration of DynamicARC, institutions can expect to broaden their treatment capabilities and patient throughput. The technology enables healthcare providers to manage a higher caseload and treat a more diverse range of patients.3,5 The integration of DynamicARC can be particularly beneficial for institutions looking to enhance their cancer treatment capabilities and improve patient outcomes.
The Future of Proton Therapy with DynamicARC
In conclusion, Dr. Rohan Deraniyagala’s vision of DynamicARC benefits in proton therapy is clear: “it will provide faster treatments, and thus a higher throughput of patients, (…) provide conformal treatment leading to less side effects, long term, (…) and increases the caseload and the type of patients that can be treated with proton therapy”. DynamicARC is not just a tool; it represents a significant leap forward in how cancer treatment can be delivered.
Read more about how DynamicARC can enhance treatment delivery through sharper, faster and simpler treatments for a wide variety of clinical cancer indications here.
Notes
Disclaimer: The statements of the healthcare professional included in this testimonial reflect only his opinion and personal experience. They do not necessarily reflect the opinion of any institution with whom he is affiliated or IBA.
* DynamicARC is the registered brand of IBA’s Proton Arc therapy solution which is currently under research and development. DynamicARC will be available for sale when regulatory clearance is received. Due to a continuous research and development program, IBA reserves the right to make changes in design, technical descriptions, and specifications of its products without prior notice. Some features are under development and may be subject to review by competent authorities.
References
- Ding X et al. The first modeling of the spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) delivery sequence and investigating its efficiency improvement. Int J Part Ther. 2022;8(4):97.
- Liu G et al. The First Modeling of the Spot-Scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) Delivery Sequence and Investigating its Efficiency Improvement in the Clinical Proton Treatment Workflow. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021;111(3):e524.
- Mein S, et al. Particle arc therapy: Status and potential. Radiother Oncol. 2024 Oct;199:110434. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2024.110434. Epub 2024 Jul 14. PMID: 39009306.
- de Jong B et al. Both S. Spot scanning proton arc therapy reduces toxicity in oropharyngeal cancer patients. Med Phys. 2023 Mar;50(3):1305-1317.
- Ding X et al. Improving dosimetric outcome for hippocampus and cochlea sparing whole brain radiotherapy using spot-scanning proton arc therapy. Acta Oncol. 2019;58(4):483-490.
- Seco J et al. “Proton Arc Reduces Range Uncertainty Effects and Improves Conformality Compared with Photon Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy in Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.” International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 87, no. 1 (2013): 188–94.
- Li X et al. Improve dosimetric outcome in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer treatment using spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy. Radiat Oncol. 2018 Feb 27;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13014-018-0981-6. PMID: 29486782; PMCID: PMC6389253
- Liu G, Zhao L, Qin A, Grills I, Deraniyagala R, Stevens C, Zhang S, Yan D, Li X, Ding X. Lung Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) Using Spot-Scanning Proton Arc (SPArc) Therapy: A Feasibility Study. Front Oncol. 2021 Apr 22;11:664455. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.664455. PMID: 33968770; PMCID: PMC8100671.
- Chang S, Liu G, Zhao L, Zheng W, Yan D, Chen P, Li X, Yang K, Deraniyagala R, Stevens C, Grills I, Chinnaiyan P, Li X, Ding X. Redefine the Role of Spot-Scanning Proton Beam Therapy for the Single Brain Metastasis Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Front Oncol. 2022 May 19;12:804036. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.804036. PMID: 35664795; PMCID: PMC9160604.